9.2 Hypernyms, Hyponyms, and the Implements Keyword
Hypernyms, Hyponyms, and Interface Inheritance
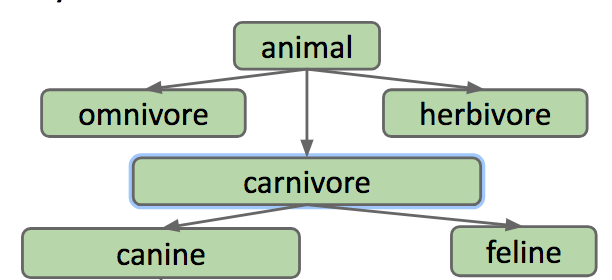
In the English language and life in general, there exist logical hierarchies to words and objects.
Dog is what is called a hypernym of poodle, malamute, husky, etc. In the reverse direction, poodle, malamute, and husky, are hyponyms of dog.
These words form a hierarchy of "is-a" relationships:
a poodle "is-a" dog
a dog "is-a" canine
a canine "is-a" carnivore
a carnivore "is-an" animal
The same hierarchy goes for SLLists and ALists! SLList and AList are both hyponyms of a more general list.
We will formalize this relationship in Java: if a SLList is a hyponym of List61B, then the SLList class is a subclass of the List61B class and the List61B class is a superclass of the SLList class.
Figure 4.1.1 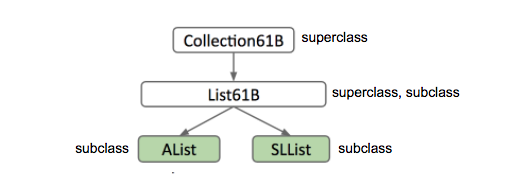
In Java, in order to express this hierarchy, we need to do two things:
Step 1: Define a type for the general list hypernym -- we will choose the name List61B.
Step 2: Specify that SLList and AList are hyponyms of that type.
The new List61B is what Java calls an interface. It is essentially a contract that specifies what a list must be able to do, but it doesn't provide any implementation for those behaviors. Can you think of why?
Here is our List61B interface. At this point, we have satisfied the first step in establishing the relationship hierarchy: creating a hypernym.
Now, to complete step 2, we need to specify that AList and SLList are hyponyms of the List61B class. In Java, we define this relationship in the class definition.
We will add to
public class AList<Item> {...}
a relationship-defining word: implements.
public class AList<Item> implements List61B<Item>{...}
implements List61B<Item> is essentially a promise. AList is saying "I promise I will have and define all the attributes and behaviors specified in the List61B interface"
Now we can edit our longest method in WordUtils to take in a List61B. Because AList and SLList share an "is-a" relationship.
Last updated